Orchestrating the new, heterogeneous robot fleet
As companies seek new use cases for robots in their supply chains, many will find themselves needing to integrate different robots from different vendors that perform different tasks.

The past few years have witnessed an explosion in interest in and use of robots within the supply chain. According to Gartner’s most recent “Supply Chain Technology User Wants and Needs Study”—a cross-industry, cross-company size, and cross-geography survey—a staggering 96% of respondents said they were investing, or were planning to invest, in robotics over the next two years.
Of those respondents, 7% had already fully deployed a robotics solution, and 29% were currently deploying one. Furthermore 93% of these current robot users said that they planned to expand the fleet size of their existing robot platforms, and 94% said they were pursuing additional use cases for robotics in their operations.
As a result of this interest, we believe there will be exponential growth in what we call the “intralogistics smart robots” (ISR) marketplace over the next decade. In fact, Gartner predicts that by 2028, 50% of large enterprises will have adopted some form of ISRs in their warehouse or manufacturing operations.
Currently, Gartner tracks 34 different categories of intralogistics smart robots. Among the most relevant categories to logistics leaders are six that we see companies deploying and having the most success with today. The categories include:
- Basic transport—This category involves autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) designed to move goods around warehouses and plants. These trainable and intelligent robots excel at moving goods long distances and can operate through multiple shifts. By using them, companies reduce the amount of time human workers waste traveling across the warehouse.
- Collaborative picking (robot to person)—For this application, a human worker and robot move through the warehouse together. The human worker picks products into bins or totes transported by the robot. This category will enhance human labor by improving picker efficiency, cycle time, and throughput. This “cobot” augmentation of human effort can leverage existing infrastructure and will be utilized in high volume/velocity picking environments such as e-commerce.
- Goods to person (G2P)—For this variation, the robots deliver multiple goods on mobile storage units (MSUs) to a stationary area, where a human picks goods for multiple orders onto another MSU. When all the orders are complete, robots deliver the MSUs to packing stations. G2P robots can eliminate wasted travel time for human workers, reducing drudgery and fatigue.
- Sortation robots—This category will be seen both in e-commerce and parcel-sorting environments and will improve order-fulfillment accuracy and agility while streamlining picking and packing operations. These robots can replace powered conveyors and are not bolted to the floor, meaning they are adaptable and reconfigurable on demand, with lower fixed infrastructure requirements.
- Robotic picking—These robotic solutions are designed to handle the most mundane pick-and-place tasks. These solutions combine robotic arms, different forms of end effectors or grippers, and 3D vision systems, all enabled by advanced machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI). Robotic picking works particularly well in environments where the items are a consistent size and shape.
- Cube robotic G2P systems—In this category, G2P robots autonomously move goods in totes or cases that are stored in a pre-built cube/grid structure. The robots also deliver these totes or cases at the appropriate time to humans at pick stations. These solutions work well for high-density and high-speed environments. For example, these applications work well in facilities with large quantities of small items that are ordered frequently. This category is scalable and adaptable and is typically delivered as a larger integrated system.
Each of these categories represents different use cases and operating models, some are designed to be stationary, others mobile; some are designed to operate alone and autonomously; while others are designed to complement human labor.
As companies seek new use cases, many will start to have different robots from different vendors performing different tasks. We believe that within the next five years more than 40% of large enterprises will have a heterogeneous fleet of ISRs in their warehouse operations. The good news is that many companies will begin to leverage ISRs in their operations. The bad news is that this creates challenges for companies. Namely, how do they integrate with and orchestrate the work of a heterogeneous fleet of robots? And how do they coordinate between different fleets?
Standardized software needed
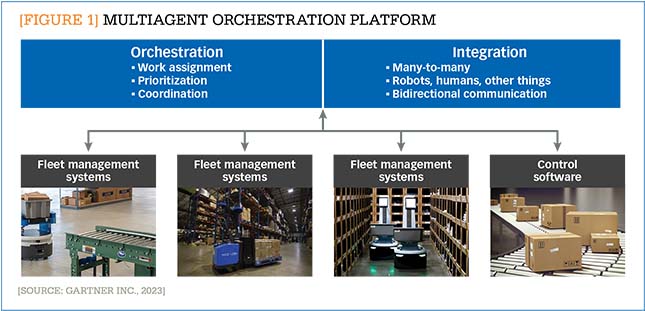
To integrate and orchestrate the work of a fleet of heterogenous robots, companies will need standardized software that can easily unite a variety of agents and robot platforms. Gartner refers to this emerging software as “multiagent orchestration platforms.” These solutions act like intelligent middleware that integrate and orchestrate work among various business applications, heterogenous fleets of operational robots, and other automated agents like doors or elevators. These solutions will assign work to the right robots based on the characteristics of the immediate tasks and will orchestrate communication between different robot platforms and other types of automation agents. (See Figure 1.)
<
[FIGURE 1] Multiagent orchestration platform
Enlarge this image
This type of software becomes increasingly necessary as the robotic environment becomes more complex. When companies invest in their first ISR platform, they will typically just create a one-off connection between their business applications—such as a warehouse management system (WMS)—and their robot provider’s fleet management system. This, while not optimal, works for one robot. However, as a company’s fleet of robots grows, simple point-to-point API (application programing interface) integration will not be enough. Companies will need an orchestration capability that can assign work to the right robots based on near-real-time information. These work assignments will need to take into consideration the characteristics of the activity and the capabilities of various automation agents. A multiagent orchestration platform will reduce the time, effort, and cost to onboard new robots. It will also reduce support cost, ultimately making organizations more efficient because work will be assigned to the robot best suited for the task. As a result of this need, we believe that by 2026, more than 50% of companies deploying intralogistics robots will adopt a multiagent orchestration platform.
Of course, most companies will not recognize the need for these types of solutions until they move beyond one or two robot platforms. Then, they may attempt to find a solution through their current WMS provider or their robot provider’s fleet management systems. These systems may or may not address the need for orchestration and integration across and between a variety of robot platforms. While some providers do offer these types of orchestration platforms, many ISR providers’ fleet management solutions are largely focused in and around their own robot offerings and are not true multiagent orchestration platforms. To be sure, many ISR providers are focusing more on software, as they are concerned that they will be commoditized by less expensive robot hardware. But we do not expect a universal fleet management platform that works across robot platforms any time soon, if ever. Consequently, for the foreseeable future, companies with heterogeneous fleets of robots will need a multiagent orchestration platform.
To identify the right platform capable of orchestrating and integrating their heterogenous robot fleet, companies should start by analyzing the integration requirements as their robot fleet expands beyond a single vendor. Along with that, they should study how work will be assigned to the various robots and other automation agents and determine what orchestration logic will be needed to support this simultaneously. Once they understand their orchestration and integration requirements, they should then look for the multiagent orchestration platform that best addresses their needs.
Related Articles
Recent Articles by Dwight Klappich
Copyright ©2024. All Rights ReservedDesign, CMS, Hosting & Web Development :: ePublishing