LMI reaches all-time low in April
Following a surge in March, economic growth in the logistics industry slowed in April to a reading of 51.3, according to the latest Logistics Manager’s Index report.
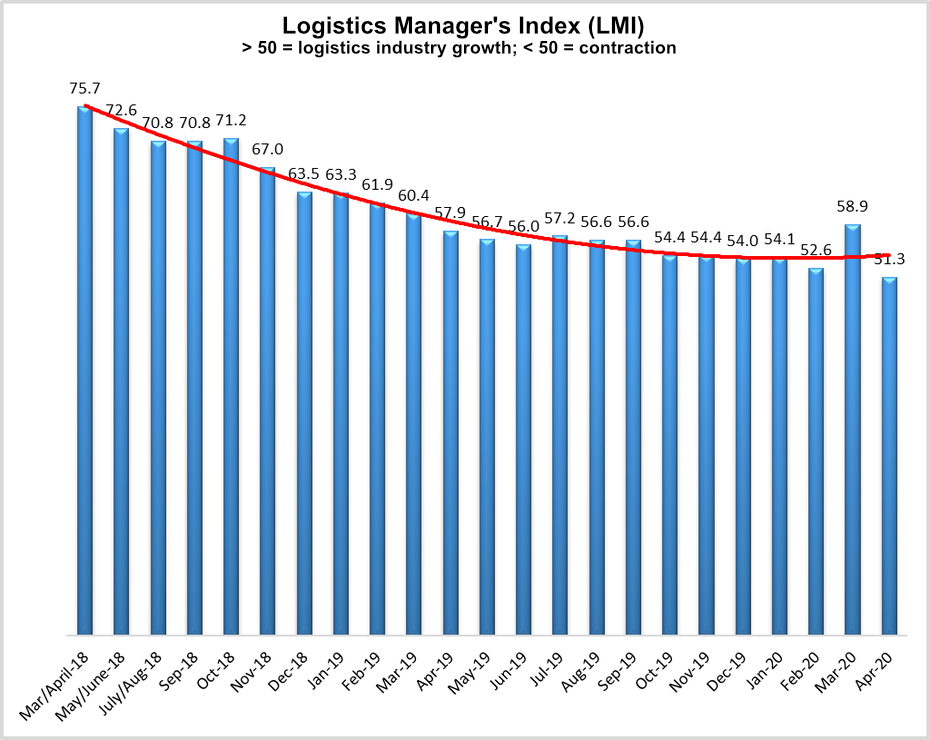
Business activity in the logistics sector slowed in April following a surge in March to reach an all-time low industry reading of 51.3, according to the latest Logistics Manager’s Index (LMI) report, released today.
The April reading is down 7.6 points compared to March, but still remains in growth territory, indicating expansion in the logistics economy. An LMI reading above 50 indicates growth in the sector; a reading below 50 indicates contraction. LMI researchers said the March surge was due to panic buying of groceries, cleaning supplies, paper products, and the like as state and local stay-at-home orders and business shutdowns took effect in response to the coronavirus outbreak.
The April results mark a return to the steady decline in activity that industry researchers have observed over the last two years. The LMI reached its high-water mark in April 2018, at 75.7.
The April 2020 reading indicates that the logistics economy is “basically holding steady,” according to LMI researcher Zac Rogers, assistant professor of supply chain management at Colorado State University. “It’s our lowest reading, but it’s still not showing contraction.”
Rogers described the April LMI as a “tale of two sectors”—transportation and warehousing. Following the surge in consumer panic buying in March, transportation has “dropped like a rock” he explained, pointing to a 15.2-point jump in transportation capacity, a record drop of nearly 28 points in transportation prices, and a more than 10-point drop in transportation utilization. This means that despite there being many trucks on the road making deliveries, “we’ve never used less of the trucks available, and getting a truck has never been cheaper,” Rogers explained.
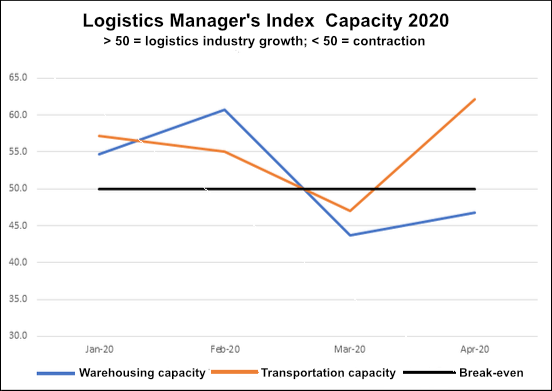
The excess capacity in transportation is a “clear indicator that demand for product movement is down,” Rogers said, adding that demand for warehousing is growing as companies deal with the effects of slowing consumer demand for pretty much anything other than groceries and similar essential items. This will lead to an offloading of inventory in the coming months, which coud trigger slowing demand for warehouse space.
“I wouldn’t be surprised to see warehousing come down over the next few months,” Rogers added.
The LMI tracks logistics industry growth overall and across eight areas: inventory levels and costs; warehousing capacity, utilization, and prices; and transportation capacity, utilization, and prices. The report is released monthly by researchers from Arizona State University, Colorado State University, Rochester Institute of Technology, Rutgers University, and the University of Nevada, Reno, in conjunction with the Council of Supply Chain Management Professionals (CSCMP).
Visit the LMI website to participate in the monthly survey.
Related Articles

Copyright ©2024. All Rights ReservedDesign, CMS, Hosting & Web Development :: ePublishing