A year after East Palestine accident, rail industry regulations are largely unchanged
Despite safety upgrades, the number of freight train accidents rose 11% over 2022, Everstream Analytics says
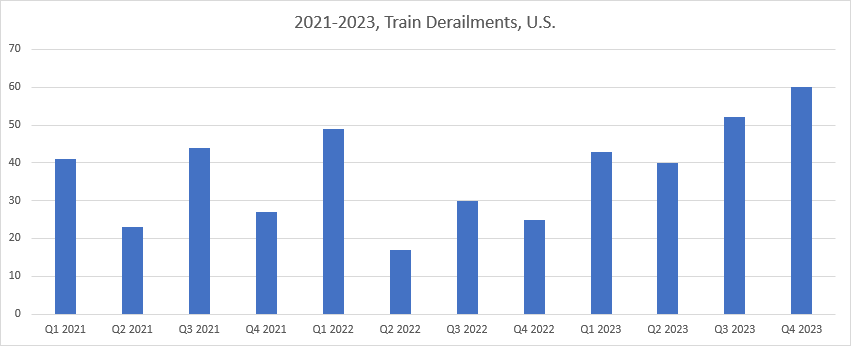
The number of train accidents in the U.S. rose in 2023, even as proposed legislation to tighten safety regulations sits idle in Congress a year after a Norfolk Southern freight train derailed and spewed chemicals in East Palestine, Ohio, according to supply chain risk analysis firm Everstream Analytics.
If that accident trend continues, it could lead to growing problems in freight operations and increasing supply chain risk. “Without a regulatory overhaul, it is likely that train accidents will continue an upward trend,” Mirko Woitzik, Global Director of Intelligence Solutions at Everstream Analytics, said in a statement. “Trains are faster, longer, and carrying more cargo than ever before, making them more susceptible to accidents. An increase in accidents will ultimately lead to cargo delivery delays and shipment unpredictability.”
Specifically, the five Class 1 freight railroads operating in the United States — Union Pacific, BNSF, CSX, Norfolk Southern, and Canadian National – reported 256 accidents on their mainlines last year through October, representing an 11% increase from the same period in 2022, the firm said. The total number of derailments increased 13.5% last year, while obstruction accidents involving a train striking an object, increased 21%.
“Following the East Palestine derailment in Q1 of ’23, the number of incidents never saw a notable drop as would have been expected – instead, the numbers saw an uptick in the second half of the year. Further, Q4 saw the highest recorded incident numbers since 2021,” Woitzik said.
After the derailment occurred in February, 2023, various oversight bodies including the U.S. Department of Justice, state of Ohio, and U.S. Congress announced plans to tighten safety rules governing the rail sector. But the highest profile initiative—the Railway Safety Act—remains stuck in committee.
“In the weeks following the disastrous event, many called for widespread reforms to train safety protocols and enforcement in the U.S. However, one year on, Congress has failed to pass any legislation to prevent similar incidents. Despite the scrutiny received in the wake of the East Palestine incident, industry regulations are largely unchanged,” Woitzik said.
Part of the reason for that status is the strict opposition to the bill that has come from rail industry trade group the Association of American Railroads (AAR), which calls the bill “problematic” and has says that voluntary changes applied by the rail companies themselves are a better solution.
As examples, AAR cited recent rail industry moves to:
- increase the frequency of hot bearing detectors (HBDs) on some routes
- establish a new industry standard of stopping and inspecting trains when an HBD reading exceeds certain temperatures
- train 20,000 first responders in local communities
- double the number of first responders with access to AskRail, which provides real-time information on rail car contents and the safe handling of those materials
- supplement railroads’ confidential reporting programs by joining the Federal Railroad Administration's voluntary C3RS program
“Since the East Palestine, Ohio train derailment, America’s freight railroads acted quickly and decisively to pursue voluntary actions to help prevent similar accidents from occurring in the future,” the AAR said in a January 26 release. “Over the past twelve months, the Class I railroads have kept, and in some cases exceeded, their promises, clearly demonstrating the industry’s commitment to lead, innovate and implement tangible safety solutions without waiting for mandates from Congress or regulators.”
Related Articles

Copyright ©2024. All Rights ReservedDesign, CMS, Hosting & Web Development :: ePublishing