McKinsey: shippers and logistics providers share common pain points
But rush to apply leading technologies leads to challenges in integrating them all together, for both transportation and warehousing
Even under difficult market conditions, both shippers and logistics providers have sustained or grown their technology investments since 2020, leaving laggards with less and less room to maneuver, according to a report from the consulting firm McKinsey & Company.
But even with money to invest, adopting new tech can be a challenge, since the technology landscape has become increasingly complex and crowded. Companies face questions about not only what value they expect from a technology but also how that technology will fit into their enterprise-level technology landscape, their day-to-day operating models, and their underlying logistics processes, McKinsey said in “Digital logistics: Technology race gathers momentum.”
The results come from a survey of more than 250 logistics leaders, representing both shippers and providers, who say that turbulent market forces are compelling companies to transform their logistics functions for greater flexibility, predictability, efficiency, and resilience.
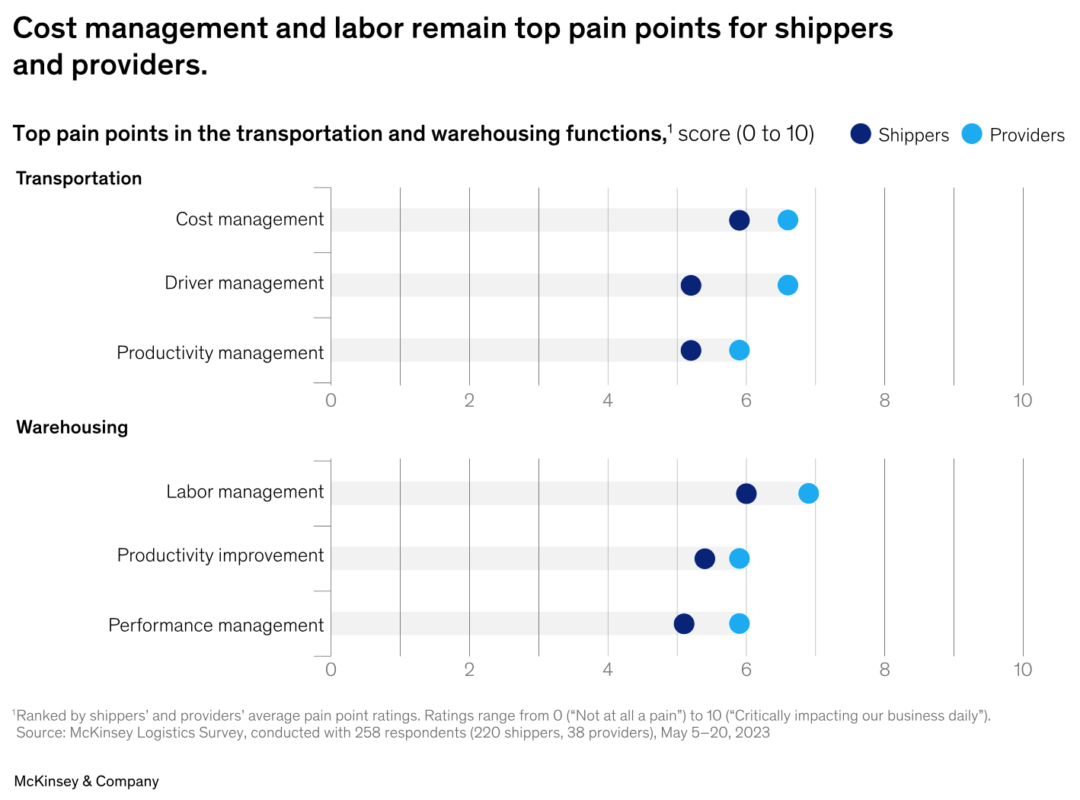
The survey also shows that both shippers and providers are moving beyond foundational technology and turning to leading-edge solutions to gain or maintain a competitive advantage. Specifically, respondents said their top pain points in transportation were: cost management, driver management, and productivity improvement. And the top headaches in warehousing were: labor management, productivity improvement, and performance management.
Interestingly, the pain points for shippers and providers are similar, McKinsey found. That implies that shippers and providers have an opportunity to address other shared challenges, particularly wherever they can coordinate and complement each other’s capabilities. This approach could lead to improved efficiency, reduced costs, and increased customer satisfaction for both parties.
Digging into the growing popularity of specific technologies, the report found platforms that are in broad, scaling, or early stages of development in each of three sectors.
In transportation, digital freight procurement and asset tracking & data mining are in broad use. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) for internal transport, enhanced driving solutions, and digital yard management are starting to scale up. And cutting-edge technologies, such as delivery drones and hydrogen vehicles, are at much earlier stages of development.
In warehousing, real-time distribution center performance management, AGV-based goods-to-person solutions, and warehouse management systems, are already in (or nearing) broad use. Digital warehouse twins, dynamic labor management, and gesture & motion tracking have proven themselves in piloting, while fully automated item picking, network digital twins, and smart shelves are still demonstrating feasibility.
And in planning, technologies in wide use include automated replenishment and data mining & automated root-cause analysis for performance management. Machine learning–based forecasting and microsegmentation are now in selective use. And digital command centers with micro-apps, which are moving out of the pilot stage, enable oversight of the entire logistics system—transportation, warehousing, and planning—all in one place.
Against that backdrop, McKinsey researchers said that shippers and providers have to balance two goals, not only selecting the right use cases, but also ensuring that their numerous transportation and warehousing solutions integrate seamlessly together. To wit, a plurality of logistics providers (34%) now have as many as eight or nine different technology solutions in their transportation tech stacks, and 37% of them have five or more solutions in their warehousing operations.
Related Articles
Copyright ©2024. All Rights ReservedDesign, CMS, Hosting & Web Development :: ePublishing