U.S. manufacturing resurgence faces headwinds
Nearshoring and reshoring activities have increased, but U.S. occupiers struggle with tight leasing market conditions, old infrastructure, and low unemployment, Cushman & Wakefield says.
A resurgence of U.S. manufacturing faces headwinds, even though nearshoring and reshoring activities have increased from both businesses and governments, according to a report from industrial real estate firm Cushman & Wakefield.
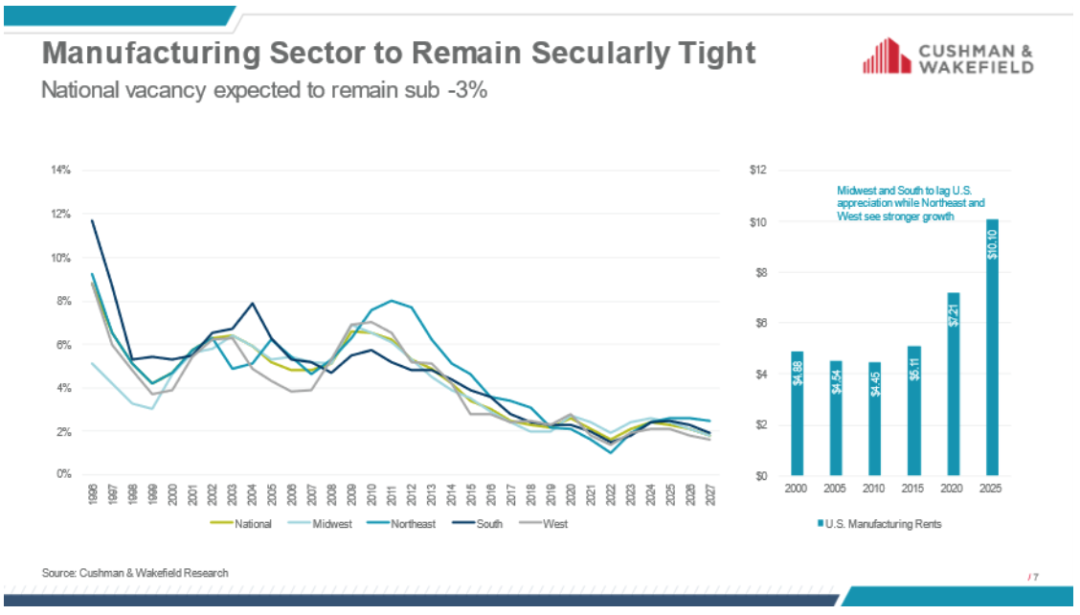
With the revived effort to begin reshoring and nearshoring manufacturing to and toward the U.S., the composition of real estate will need to change, the firm said. Currently, manufacturing vacancy makes up 10.3% of the country's total available space and that is not likely to improve anytime soon, as tight leasing market conditions will be an issue for occupiers who have not already secured their facilities. Specifically, there are only 80 million square feet of space currently under construction, of which half will be owner-occupied and 25% is non-owner-occupied build-to-suit.
“Both governments and the private sector became more aware of the economic, financial and social impacts that disruption to supply chains can have — along with increases in protectionism that predated the pandemic — and the increased emphasis placed on sustainable energy supply chains, nearshoring and reshoring considerations have intensified for businesses and governments alike,” Ben Harris, Senior Managing Director, Logistics & Industrial Services – Americas, said in a release.
Alongside the real estate component, other parts of the U.S. infrastructure will need to change, the report said. Manufacturing requires a lot of power, and many greenfield land sites lack sufficient power to host the manufacturing sites needed. Limited land options for commercial real estate make selecting a new site difficult, but it will be more challenging for manufacturing users. In addition to struggles with power, the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE) gave the nation's infrastructure a grade of C-minus on its 2021 quadrennial infrastructure report card.
In addition, U.S. manufacturing employment is up, but still lags overall national trends. The statistics show that manufacturing sector employment rose to 13 million as of midyear 2023, its highest level since 2008. That represents only a 1.3% increase from the same period in 2019, compared to a 3.5% increase in employment across all sectors, the firm said.
“The U.S. has a long way to go before larger reshoring and nearshoring trends take hold,” said David Smith, Head of Americas Insights. “Manufacturers need to decide if it makes sense to relocate parts or the entirety of an operation and if the U.S. is the right place. As it becomes more possible to diversify supply chains and bring manufacturing back to the U.S., it will be important to consider the state of manufacturing real estate. Working strategically on location, understanding labor needs, and the cost of operations and materials will be more important than ever, and the planning should start now.”
Another report this week likewise concluded that geopolitical uncertainties and high U.S. tariffs are driving a significant shift away from China as the primary export platform for North American markets, according to a study from Boston Consulting Group (BCG) titled “Harnessing the Tectonic Shifts in Global Manufacturing.”
Accordingly, reshoring to the U.S. is a clear trend, but a lot of manufacturing business is also relocating to and Mexico, India, and Southeast Asia. Those regions are rapidly emerging as future export manufacturing powerhouses, thanks to their deep labor pools and growing scale and capabilities across diverse industries, BCG said. For example, from 2018 through 2022, U.S. goods imports declined by 10% from China in inflation-adjusted terms, but they rose by 18% from Mexico, by 44% from India, and by 65% from the ten countries of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN).
"Changing geopolitics, the evolution of relative cost structures, more frequent and high-impact disruptions, and the push for decarbonization, among other factors, will lead to a massive restructuring of global supply chain networks over the next decade," Ravi Srivastava, global leader of BCG's Operations practice and a coauthor of the report, said in a release. "Companies need to fundamentally rethink their manufacturing and distribution networks, build capabilities in new geographies, leverage government incentives, and establish new relationships across the supplier ecosystem to enhance their competitive advantage and protect their business."
Related Articles

Copyright ©2024. All Rights ReservedDesign, CMS, Hosting & Web Development :: ePublishing