USPS plan would slow package delivery for long-distance hauls
If approved, service would carry more packages by truck instead of plane, changing three-day delivery plan to a two-to-five day window.
The U.S. Postal Service is proposing a plan to save money by slowing its delivery speed for parcels traveling more miles, converting its delivery guarantee for First-Class Package Service (FCPS) from the current umbrella 3-day service plan for the continental U.S. to a range of two to five days based on distance.
If that plan is approved, the USPS would transport more packages by truck instead of plane, saying that mode is more reliable and affordable, helping it to improve on-time delivery rates and offer lower rates to shippers. “These changes position us to better utilize our existing ground network, in which the average truck currently runs approximately 40% full. By moving more packages via surface transportation than air, we will improve service reliability, increase efficiency, and reduce costs,” the service said in a release.
The change would be one more step in Postmaster General Louis DeJoy’s 10-year plan to balance the books of the infamously money-losing agency, following his announcement in May that he had requested regulatory approval to hike stamp prices for first class mail from 55 cents to 58 cents beginning August 29.
In DeJoy’s vision, running the USPS more like a private business than a government service can help it compete with other carriers and reap greater profit from trends like the jump in e-commerce packages that have been filling its mail trucks in recent years, even as its letter-carrying revenue has plummeted in an era where many people and businesses prefer to send email. If all of DeJoy’s suggestions are implemented, that overhaul aims to reverse a projected $160 billion in losses over the next 10 years while enabling $40 billion in capital investments in areas like its mail and package processing network, facility upgrades, and procurement of new processing equipment.
However, the postmaster general cannot make those sweeping changes by executive action. Rather, many changes to postal service policies must be approved by U.S. Congress or by oversight boards appointed by the President. Thus, the agency has not actually slowed its package delivery yet, but simply took a first step “by initiating the process of requesting an advisory opinion from the Postal Regulatory Commission to evaluate its proposal.”
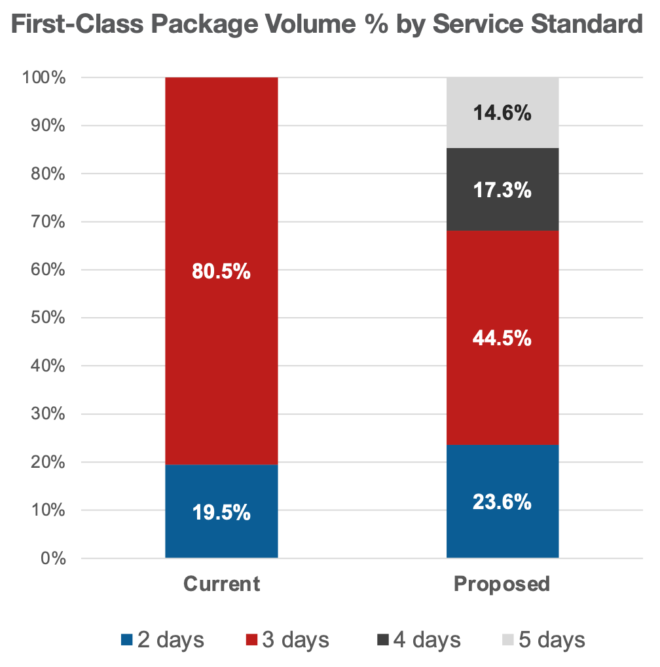
If the commission approves the plan to change its package delivery speeds, USPS said 68% of those packages would keep their current delivery standard of 2-3 days while 32% could have a day or two of transit time added to cover a greater distance.
“Whether it’s 300 miles or 3,000 miles, the current standard requires 3-day service for any destination within the contiguous U.S. with a drive time greater than 6 hours. This is unattainable and forces us to overly rely on air transportation, yielding unreliable service,” USPS said in a release. "With this change of offering 2- to 5-day service based on distance, we will improve service reliability and predictability for customers, while also driving efficiencies across the Postal Service network.”
Of the 32% of packages taking longer to reach their destinations, about half of the agency’s 3-day package volume would shift to 4-day service and the other half would shift to a 5-day service standard. The change could also allow some packages to actually speed up, with an estimated 4% being upgraded to 2-day service in a move that would better position USPS in the fast-growing market for 1-2 day delivery, the service said.
Related Articles

Copyright ©2024. All Rights ReservedDesign, CMS, Hosting & Web Development :: ePublishing